Water conservation is increasingly becoming a strategic imperative for commercial-pool operations.
At a time when the issue of water scarcity and access to safe water has become central for the UN’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, facilities for leisure, wellness, hospitality and sports where water is fundamental must necessarily implement strategies for water conservation.
In this context, addressing water conservation is fundamental, considering large-scale pools consume significant volumes of water, not only for filling, but also due to losses caused by evaporation, filtration backwash, piping leaks, and regular renewal cycles.
Crucially, the pool industry today has access to a strong toolkit of solutions that allow operators to reduce water consumption and reuse this key resource, making installations both cost-effective and environmentally sustainable. Let’s take a look at the wide range of strategies for water conservation in pools.
Dive deeper with the eBook
What are key water conservation interventions that swimming pools can implement?
Harnessing alternate water sources: rainwater & reuse
One of the foundational steps in water conservation for swimming pools is to minimise reliance on fresh mains water.
In this context, there are two key strategies that commercial swimming pool operators may implement:
- With rainwater being a source of naturally soft water, rainwater harvesting system can become a key to reduce dependence on municipal supply. These systems enable the collection of rainfall from roof catchments and adjacent hard surfaces, to then store it and use it to top up pools or auxiliary systems.
- Water recycling systems can enable the reuse of greywater (e.g., from showers, deck washing or changing rooms) and water from filter back-washes. Through the right technology, these water sources are treated and reused for secondary purposes, including irrigation, cleaning or even as pool make-up water (a use that is often subject to specific regulation).

Opting for regenerative filters & backwash reuse technologies to minimise water losses
An often overlooked contributor to water waste is the periodic backwashing required by traditional sand-based filtration systems, which use fresh water to clean the filter media.
Pool operators looking to elevate their water conservation efforts today are presented with several options to avoid this:
- Updating to modern filtration alternatives such as regenerative filters, which can cut back-wash water consumption by up to 90%. A key reduction due to these filters’ use of vibration, air-scouring or minimal water to clean the media, which dramatically reduces water lost to backwashing.
- Establishing systems that capture backwash effluent, treat it and reuse it for non-potable functions, including landscape irrigation, flushing toilets, or even pool refilling under certain conditions.
Implementing smart water management via digital twin technology
Beyond hardware, digital infrastructure is emerging as a key ally to facilitate water conservation in commercial pool facilities. In this context, digital twin technologies are being applied to the aquatic sector to guarantee an efficient and sustainable use of water.
At their core, digital twins are a virtual representation of a physical system that continuously updates using real-time sensor data. This technology offers access to a digital version of the pool that mirrors different pool parameters in real time.
A look at Fluidra’s Datapool Digital Twin solution illustrates the implications of digital twins for water conservation: by modelling pool operations (occupancy, water/energy consumption, temperature, weather influences) and integrating real-time data, the tool provides facility managers with actionable insights that, ultimately, allow them to reduce water and energy consumption by 10-40%.
A key addition for water conservation that has implications on other areas, including possibilities such as predictive maintenance, the simulation of “what-if” scenarios (e.g., filtration adjustments, load variations) and valuable data for optimizing water asset performance.
A number of advanced operations that enable benefits for commercial pool installations such as:
- Fewer unexpected losses due to leaks or inefficient cycles.
- More precise chemical and filtration dosing.
- Smarter refill policies tied to predicted demand and weather.
Optimising hydraulics and piping to reduce losses
Water conservation isn’t just about reuse, but also about reducing losses and inefficiencies in any given system. From this perspective, hydraulics and piping must be closely examined when it comes to improving water conservation efforts.
Within commercial pool setups, long or poorly sized piping runs contribute to water (and heat) loss, pressure drop, longer circulation times and increased risk of leaks. Conversely, designing shorter, optimally sized piping connections and minimising unnecessary bends or length can reduce both water and energy losses.
As such, as a general rule, the fewer the loop losses and the shorter the circulation distance, the better the overall hydronic efficiency, hence reduced water turnover needs and less top-up.
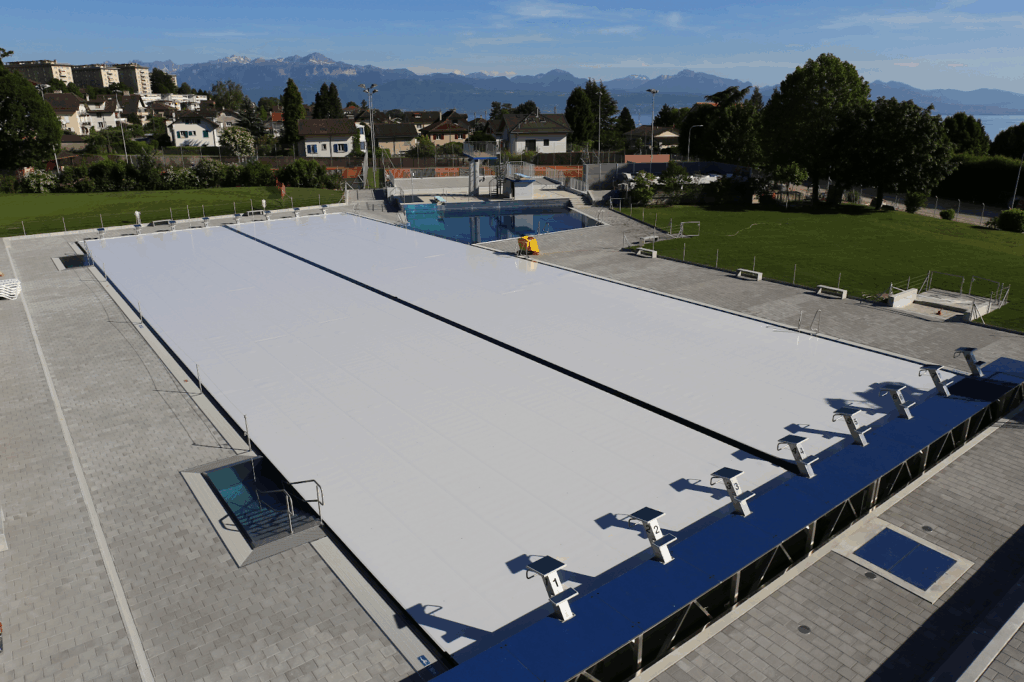

Installing pool covers to reduce evaporation
Evaporation from pool surfaces is a major and often underestimated cause of water losses, especially in outdoor or semi-outdoor commercial installations. In fact, installing a thermal or automatic pool cover can reduce evaporation losses by up to 90%.
The additional advantages of pool covers beyond water savings should also be taken into account, including:
- Capacities for heat retention, which can significantly cut heating demand.
- Reduced chemical consumption, since less freshwater top-up means fewer chemicals are needed to rebalance pool chemistry.
Heat recovery and reuse options for pool-water systems
Commercial pool installations increasingly look at waste-heat recovery systems as part of their efforts to elevate sustainability and efficiency in facilities.
Though less widely documented in pool-specific literature, this approach applies circular economy logic to pool environments, allowing facilities to transform what would otherwise be waste into a valuable resource. A revolutionary approach that takes yet another step towards the positive pool concept.
One interesting model worth considering is based on harnessing heat from adjacent facilities and redirecting it to pool water heating systems. As such, heat generated at data centers, HVAC exhaust or solar panels can all be employed as a sustainable, circular source of energy for pools.
Aside from the obvious improvement of heat energy sources, recovering waste heat can indirectly support water conservation efforts, as the pool’s reliance on fresh water (and associated energy demands to heat that water) is reduced.
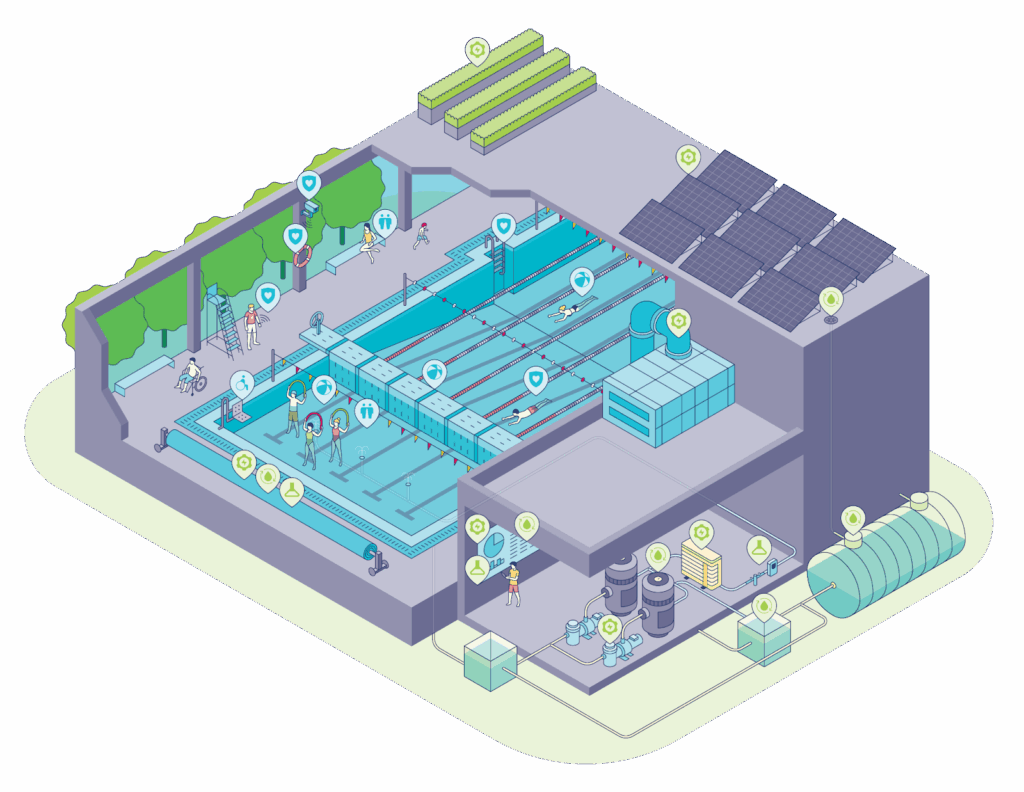
Pulling it all together: water conservation as a key step towards the “positive pool” approach
Applied correctly, these tools not only guarantee more cost-efficient swimming pool operations, but also help commercial pools build a strong strategic advantage, a social hub for communities and a more environment-friendly society.
This is where the concept of the “Positive Pool” comes in. A term for commercial pools that go beyond simply reducing their environmental impact and make it their goal to have a net positive effect from a broad perspective, in terms of water conservation but also energy use, chemicals, and social value.
Within that framework, we’ve outlined the key strategies allowing operators to move towards the positive pool framework in terms of water conservation:
- Use rainwater harvesting and capture backwash effluents.
- Install regenerative filters and water reuse solutions.
- Deploy digital twin systems (e.g., Datapool) to manage pools efficiently.
- Design hydraulics with leak monitoring and efficient circulation.
- Use pool covers to slash evaporation and top-up requirements.
- Incorporate waste-heat recovery systems to reduce water needs.
All in all, coupling smart reuse and reduction strategies with intelligent management gives pools a competitive, lasting advantage. An holistic strategy that illustrates how swimming pools are moving towards a new model where every drop counts.
FAQs about water conservation
What is water conservation?
Water conservation refers to the set of practices that aim at using water efficiently and responsibly to reduce unnecessary waste and ensure a sustainable supply for current and future needs. As such, it can involve efforts to both preserve the quantity and quality of water in natural sources (like rivers, lakes, and aquifers), as well as to reduce water use in industries, agriculture and homes.
What are the 5 Rs of water conservation?
Following the framework of the 5 Rs for a circular economy, several institutions have referred to the 5 Rs of water conservation. While there isn’t a single approach to the 5 Rs of water, it has been described as follows:
- Reduce water waste by available means and technologies
- Reuse water resources before considering them waste
- Recycle waste water to promote new uses
- Refuse practices that promote irresponsible water use
- Repurpose by finding alternative uses to water resources that have been often considered as waste
Is a swimming pool environmentally friendly?
While conventional swimming pools are often designed without taking water conservation and other environmental practices into account, a number of technologies and strategies have emerged that are allowing operators to move towards more sustainable models. From the water conservation strategies mentioned above to the reduction of chemical and energy use, as well as a more natural approach to water treatment, steps can be taken to significantly improve swimming pool’s impact and move towards the positive pool concept.
